The enterprise master patient index is a database that maintains a definitive record of all patients within a healthcare organization. It is used within an overall process called patient identity management in healthcare. The EMPI is used to positively identify patients for the purpose of providing care, processing billing, and the exchange of data among other entities. Sometimes called the corporate ID, the purpose of the EMPI is to ensure that all patient data is accurately and consistently recorded and maintained, and to prevent duplicate records or errors in patient identification. It is also used to facilitate the exchange of patient information between different healthcare providers, such as when a patient is transferred from one facility to another or with the use of health data exchanges.
EMPI vs Medical Record Number
So, what is the difference between the EMPI and the patient MRN? The EMPI differs in a couple of ways in that it 1) supersedes the MRN, and 2) is not typically known or used directly by patients. Simply put, the EMPI is the definitive identifier of a given patient across all entities. Let’s look at a practical scenario where a master patient identifier is needed. In the graphic below we have two competing hospitals in the same region: Saint Mary’s Hospital and Saint John’s Hospital.
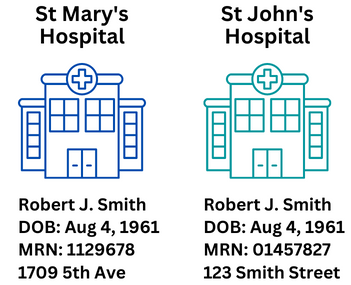
The two hospital systems have different electronic health records and billing systems. There are patients who get most of their care at one or the other, but there are also many patients who get seen at both hospitals. St. Mary’s uses a 7 digit MRN, while St. John’s uses an 8 digit MRN that includes a leading zero. The patient examples of Robert J. Smith are two different people who share the same name and birthdate. Everything is fine until the boards of both hospitals decide to merge to become one corporate entity at two locations. In addition to migrating one or both hospitals to the same EHR platform, the newly-formed organization also has to come up with a way to merge their patient lists without making any errors in duplication or misidentification. The existing MRNs and all other historical data must be retained. The patient example above will result in two new EMPIs because they are two different people.
In this next example, we have a patient who has records at both hospitals with different MRNs, but are actually the same person:
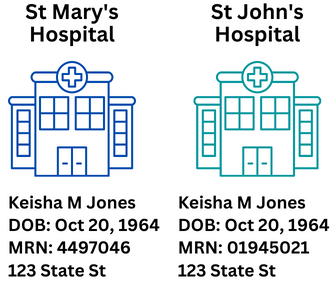
This patient will get one master patient index number.
MPI Implementation
The process for the organization will be to implement an enterprise master patient index for all patients from both hospitals. Here are some of the steps that will be taken:
- Export the entire patient database from both hospitals
- Run the patient databases through the EMPI software, which uses several algorithms to find matches:
- A deterministic algorithm looks for an exact match on data such as name, date of birth, SSN, gender, and address. This is the easy part. If the data points don’t match, then the next and more complicated level of matching happens
- The more advanced probabilistic algorithm then takes over, looking for approximate matches. It compares the same items of two records and assigns a weight indicating how closely those items match. For example, John and Johnathan, or Robert and Bob would be a pretty close match. The result would carry a weight depending on the level of matching. The same is done to all other data items, and then all weights are summed up. The final score is compared against a set of thresholds and automatically categorized into different groups.
- Next, there will be a process of referential matching that may occur against the same public databases that credit reporting agencies use. You may have seen this if you applied for a credit card online and had the application ask you a question about a business, house, or car that you owned many years ago. As creepy is this it to most of us, the process of referential matching works well in the EMPI process.
- By the time the various algorithms have done their jobs, the organization is hopefully left with very few records that may need to be cleaned up. Some of this cleanup work is done by the EMPI software. Finally, there may be some (but hopefully very few) records that need to be reviewed and fixed by actual people on the technology and/or health information systems teams.
- With a clean master patient index list, the software is now ready to create a unique identifier for each patient. The EHR data team will have found the item in the patients table to use, and the function will be performed to insert the values back into the EHR system and create a copy of the master patient index database.
As with any major project, the EHR data will need to be first imported on just a few records in a testing environment, and then into a larger number of records on a copy of the production database. Finally, the data will then be imported into the live EHR patients database or database table. You can read more on how different systems environments are set up in this post on healthcare IT environments.
After the initial implementation, the EMPI system may run in the background, constantly looking for variances in patient records. The EMPI will typically be used to notify users of any potential identification errors that may come up while providing care of performing other functions. When duplicates are found, the health information management staff and/or analysts will perform functions to merge the duplicate records.
Duplicate patient warning from DrChrono
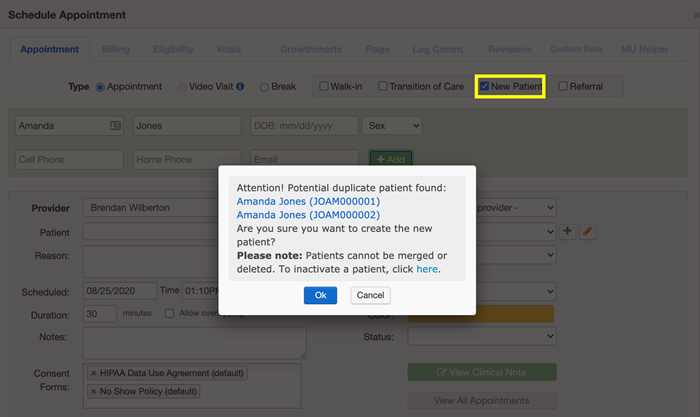
A real-world example of a successful EMPI implementation is this case study from the Idaho health information exchange, where they greatly reduced their duplication rate.
EMPI Software Vendors
While most major electronic health records systems have their own built in identity management systems, many organizations choose to use vendors that specialize in patient identity management. Some of the EMPI/patient identity management vendors are:
- Altexsoft
- Argo
- Experian Health
- HealthViewX
- Imprivata
- InterSystems
- LexisNexis
- Lyniate
- MEDecision
- QuadraMed
- Verato
Next Up:

Read More


